Table of Contents
While every blogger has many small sites, it is his one big site which feels like his own baby. And seeing that one site grow and reach the audience from multiple countries is one of the best feelings any blogger can have.
However, with the increasing competition in the blogging world, you have to deliver the best service to your user and make every aspect of your site the best possible, otherwise, the hard-earned fame of your website can fade away easily.

One important aspect of your site performance is the loading speed which is also essential for SERP. Although managing a site speed could be a major problem if your audience comes from many different parts of the world, and this is where CDNs step in.
What is a CDN?
A CDN or Content Distribution Network is basically a group of servers scattered throughout the world. When you set up your site to load through a CDN Network, it automatically detects the nearest server to the user and loads content from that, thus decreasing the page loading time.
For example, if you are hosting your site on a server located in the United States or Canada, and a Japanese user opens your site, then it will take a longer time to load your site’s content due to geographical distance.
But when you set up a CDN which has servers in multiple places, your site will load from a nearer server for example somewhere in Asia thus reducing the loading time and increasing your site’s performance.
Who should use a CDN?
Whenever the question of using a CDN comes in, there is one basic questions that crosses one’s mind which is who should use a CDN? or why should I use a CDN?

Of course, Page Loading Speed is one major factor in today’s SEO and you would like to ensure that your user gets the best experience while browsing your site, but that doesn’t necessarily mean you need a CDN for each one of your sites.
CDN is most effective for the sites which are targeting audience from multiple countries from very different geographical locations.
For example, if you have a site, with which you target mainly audience from the USA but you also get some audience from other countries which you are not targeting then you don’t need CDN. For such a site, a hosting plan with server location near or within America will do the job.
But if you are targeting audience from USA and Japan which are far away from each other then you may want to use a CDN which has servers near both countries so the audience from both countries receives fast speed while visiting your website.
How to use CDN?
There is one you need to understand before we answer the question of How to use CDN and that is how CDN works. As we said before CDN delivers the content to the end user from his nearest server, thus making the process faster.
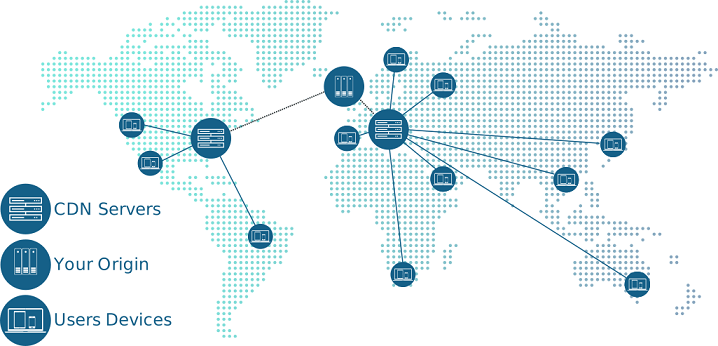
But it doesn’t mean every CDN server hosts all the files of your web page. Instead, the server is set to get the content from a ‘Host Server’ which actually hosts all your content. In most cases, a Host Server is a server where your website is originally hosted.
Another thing to understand is that the CDN servers deliver content in fragments and not as a whole web page. Meaning when a user visits a web page of your site, then the whole web page does not come from CDN servers.
Instead, the static content such as Images and Java scripts are loaded from the CDN servers one by one. You can also set up other content such as text or Links to load from CDN servers as well, but most people don’t do it.
Talking about the setup, previously you needed to set up each and every Url you want to be fetched from a CDN server on both your site and on the CDN server, For example, if your web page contains an image named Image.png, and you upload it normally, it will have an URL something like
http://websitename.com/img/image.png
But after configuring it for being fetched from the closest CDN server, you replace the URL with http://cdn.CDNwebsite.com/img/image.png. You’ll also need to update your DNS setting to point towards the CDN server in many cases.
After this, you open your CDN account and configure the Image to either be hosted at the CDN server (which costs extra money) or being fetched from the host server. Once fetched, the servers keep a cached version of the content so the next time a user requests it, it loads much faster.
Although nowadays there are many plugins available for WordPress blogs which can automate this process and lessen your burden. If you are using any other platform you might have to set up the URL of images and the source files differently which varies depending on which CDN network you are using.
Best Free CDN Networks
While using a paid resource is always considered the best option, there are cases when you can rely on free service and save your money.
That’s why here is a list of best free CDN networks which you can use:
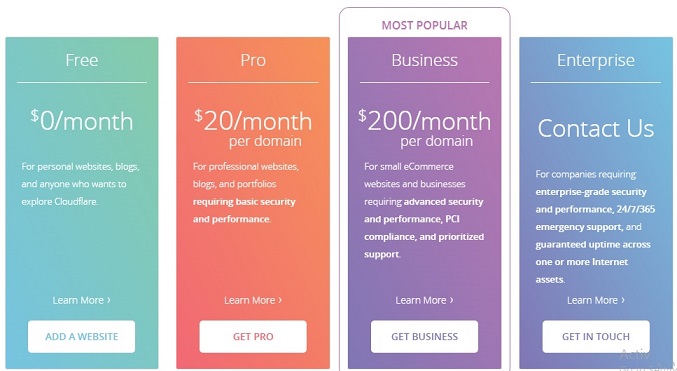
1. CloudFlare- Global Content Delivery Network
For any professional blogger, CloudFair is not a new name. It protects and fastens thousands of website around the internet and you can definitely rely on it for making your website faster.
And with over 23 data centres across the globe, CloudFlare is a wise choice for CDN, doesn’t matter the audience of which country or countries you are targeting your site with
2. Photon
Jetpack is considered and essential plugin for the majority of WordPress Blogs as it offers a wide range of features to the user. Although one lesser known feature offered by the developers of Jetpack is their free CDN network known as Photon.
The great thing is that it comes bundled with the Jetpack Plugin and to activate the service all you have to do is enable the Photon module inside the Plugin’s configuration.
3. Amazon CloudFront
Amazon is a trusted brand all over the world and among the various services it provides to bloggers and internet marketers, there is also a CDN service known as Amazon CloudFront.
If supports almost all kinds of files including images and videos and also offers a free trial for one year with some bandwidth and page view limitation. After that, you can buy a premium subscription as per your needs.

4. SwarmCDN
SwarmCDN is a relatively new service but it’s very good if you are looking to try a best free CDN network without paying for it, or if your site contains fewer web pages containing mainly images but serves a global audience.
It offers a basic free plan which gives you 10 GB of Bandwidth per month and supports more than 196 countries worldwide. The Overage charges are not very high as well so they won’t make a hole in your pocket.
5. Incapsula
The final entry in the list would be Incapsula which is known as one of the best free CDN networks among bloggers. They have a free plan which includes many useful features such as Bot Protection and Access Control and the premium plans only adds to this list.
The only downside of the free plan is that it does not include any support and for any help, you are dependent on the Incapsula community which may cause a problem if you are a first time user.

Wrap up
This was our complete guide on CDN. We hope it helped you understand the concept and usage of the Content Delivery Network. If you still have any questions left, do ask us in the comments section and we’ll try to reply as soon as possible.




